Hyper-V vs VMware
First of all, virtualisation continues to be one of the hottest company IT trends. Gartner estimates that many organizations have virtualized more than 75 per cent of server workloads. Whether your company has already invested heavily in the cloud, or is planning a first-time move, considering a hypervisor’s role in your overall experience may be important.
Furthermore, a hypervisor is the program, firmware, or hardware device that generates and operates virtual machines. The hypervisor provides virtual or guest operating systems to virtual machines and controls these virtual operating environments, which can consist of several operating systems, to be run. Morever, the right hypervisor will guarantee ease of use, flexible allocation of resources and minimal disruption to each of the operating systems in use.
Finally, in hypervisors, two of the most common options include vSphere, a VMware application, and Microsoft’s Hyper-V. Join us as we analyse Hyper-V and VMware’s pros, drawbacks, and costs, so you can determine which one is better in you.
What is Hyper-V?
Microsoft Hyper-V is design to provide “Enterprise-class Virtualization” for data centre or hybrid cloud organizations. Otherwise, for companies that want to virtualize workloads, create a private cloud, scale services through a public cloud or combine all three, this option is a common choice.
Next, Hyper-V is integrated into Windows Server, or can be deployed as a standalone server, known as the Hyper-V System, which can also ease the learning curve for virtualization managers who already have experience and history with Microsoft products. Therefore, this offers a single range of integrated management tools, whether companies choose to move to physical servers, a private cloud, a public cloud, or a “hybrid” combination of these three alternatives.
Hyper-V Pros
- Can deploy new virtual servers in minutes
- Maintenance does not result in downtime
- Simple live migrations
- Easy backups
- Comprehensive security through Windows Active Directory
- Lower priced
Hyper-V Cons
- Hyper-V (2012R2) supports a limited number of guest OS choices: see here for a comprehensive list.
- Requires Windows OS upgrades during product lifetime
- Poor or missing support for RemoteFX and Service Templates in System Centre Virtual Machine Manager 2012 R2
What is VMware vSphere?
First of all, VMware vSphere is a popular choice of hypervisors for organizations hoping to reach some degree of virtualisation. Now on version 6.0, vSphere is highly configurable, which can make it an attractive choice for companies that either go fully virtual or choose a hybrid approach.
Next, VSphere is available in several different flavors, depending on organizational needs. Then, VSphere Standard, Enterprise Plus and Operations Management Enterprise Plus provide different capabilities and degrees of fault tolerance, enabling companies to select the best available coverage for their requirements and growth objectives.
VMware vSphere Pros
- Intuitive use
- High-quality support availability
- May be an optimal fit for major enterprises
- Broad OS support
- Offers access to governance capabilities
- Transparent page sharing
- Offers higher guests per host (512 vs. 384)
VMware vSphere Cons
- Free and trial versions do not offer full functionality
- Reported steep learning curve
VMware vSphere vs Hyper-V: another factor to consider
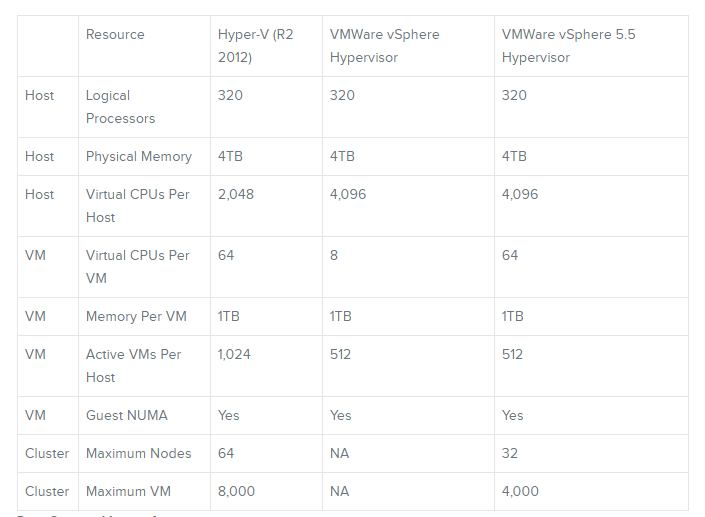
Scalability
The scalability factor of Hyper-V slightly exceeds vSphere. The maximum potential of each factor is detailed in the table below:
Design Advantages and Disadvantages
Hyper-V
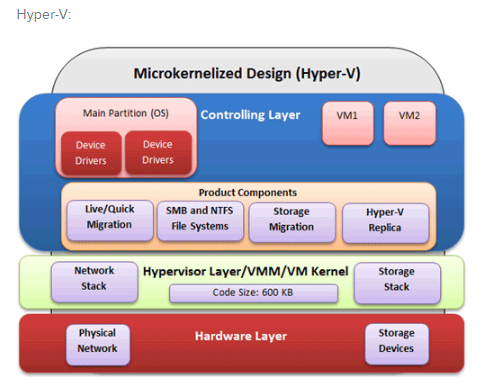
Advantages:
- For each device Hypervisor Layer or VMM Kernal does not require device drivers.
- Minimized surface of attack because layer Hpyervisor lacks APIs
- Hypervisor layer requires less overhead for maintaining device drivers.
- Any other server roles can be installed in controlling layer.
- Requires less initialization time than VMware
- Hyperviser-aware system drivers don’t need to.
- System drivers that run in “controlling layer” can be enabled in OS.
Disadvantages:
- Controlling Layer includes an OS that is enabled before Hypervisor can work.
- When the layer control OS crashes, all VMs fail.
- Controlling layer allows for more overhead.
- Safety relies on the Windows safety updates program, which allows all the VMS to be taken offline or moved to a different node to prevent downtime.
VMWare
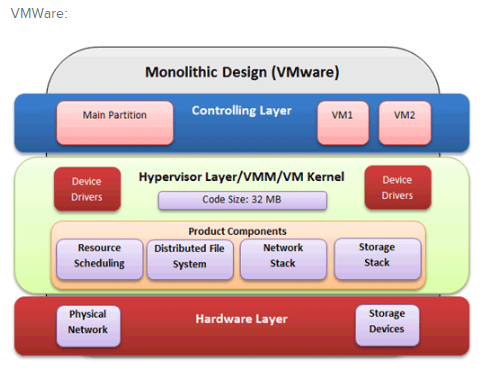
Advantages:
- No OS required to control all components of virtualization.
- No security patches needed.
Disadvantages:
- Only works on supported hardware.
- Requires more initialization time.
- Corrupted code injected in Hypervisor layer can cause delays.
Operating System Support
VMware supported Operating Systems such as :
- Oracle Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3 Quarterly Update 3
- Asianux 4 SP4
- Solaris 11.2
- Ubuntu 12.04.5
- Ubuntu 14.04.1
- Oracle Linux 7
- FreeBSD 9.3
- Mac OS X 10.10
Hyper-V will support Windows Operating Systems such as :
- CentOS
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Debian
- Oracle Linux
- SUSE
- Ubuntu
- FreeBSD
Performance
Firstly, academic research was carried out to assess the efficiency of Hyper-V, VMware. Furthermore, according to the authors of the resulting paper, “we performed performance tests using different scenarios for each approach to virtualization enabled by the latest versions of the hypervisors described.”
In the conclusion, the results indicated VMware was outperformed by Hyper-V based on performance factors. So, clear insight into the researchers ‘ results of each individual study, their methods of investigation and their conclusions.



